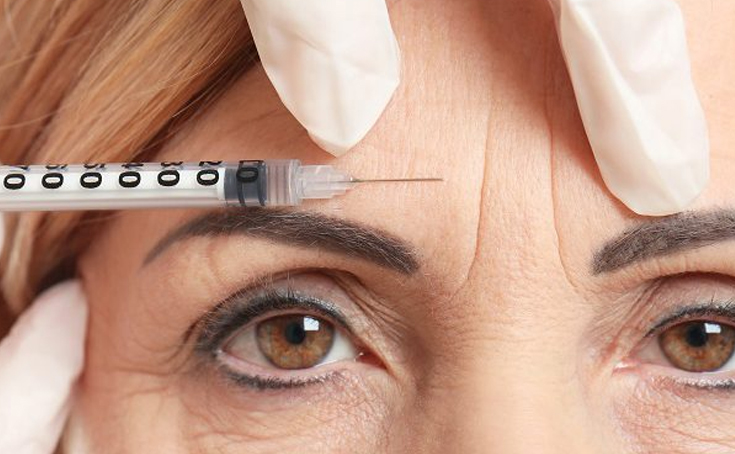
Botox Injections
Botox injections are a popular non-surgical cosmetic and therapeutic treatment that uses botulinum toxin, a purified neurotoxic protein derived from Clostridium botulinum bacteria. These injections temporarily relax muscles by blocking nerve signals, effectively reducing wrinkles and fine lines on the face. In addition to aesthetic applications, Botox is widely used for medical purposes, such as treating chronic migraines, excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), muscle spasms, overactive bladder, and certain neurological conditions.
Administered by a trained medical professional, Botox is injected directly into targeted muscles or glands. The effects typically last three to four months, after which the procedure can be repeated for sustained results.
Symptoms:
- Aesthetic: Forehead lines, crow’s feet (lines around the eyes), frown lines, and neck bands.
- Medical:
Chronic migraines (15+ headache days per month). - Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating, especially underarms).
- Cervical dystonia (neck muscle spasms).
- Strabismus (misaligned eyes).
- Blepharospasm (eyelid twitching).
- Overactive bladder symptoms.
Causes:
- Aesthetic: Wrinkles and lines caused by repetitive facial expressions, aging, and loss of skin elasticity.
- Medical:
Neurological disorders causing muscle spasticity or contractions.
Excessive nerve activity leading to conditions like hyperhidrosis or migraines.
Risks and Precautions:
While generally safe when administered correctly, Botox can cause side effects such as pain at the injection site, headache, temporary drooping of the eyelids or brows, and flu-like symptoms. Rarely, complications like difficulty swallowing or breathing may occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.

